Receding gum: risk factors, prevention, and treatment
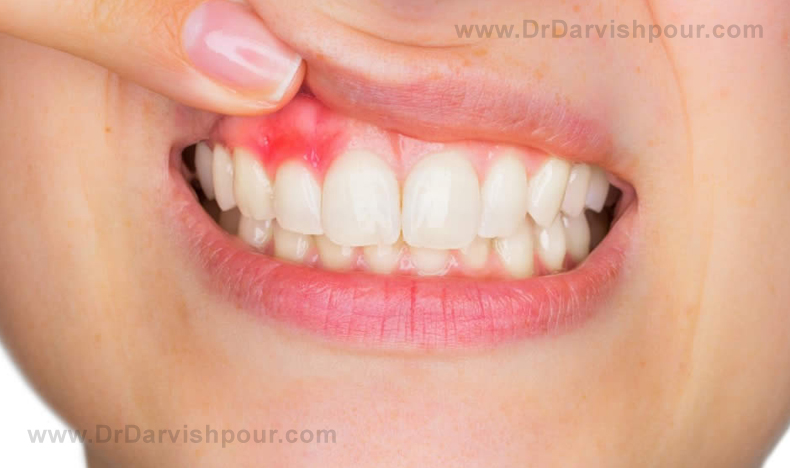
When the margin of the gum tissue surrounding your teeth wears away, pull back, showing more of the tooth or your tooth’s root, receding gum will occur. In this condition, the gap between your teeth and gum line, make a good room for disease-causing bacteria to grow up.
For some decades, it was believed that the receding gum is a stage of the aging process but today the supporting evidence for this statement is weak. The aging process may develop the risk of receding gum but it doesn’t mean aging causes gum recession. Normally, the tooth friction is associated with permanent receding because of aging and if it leaves untreated, the gum destruction can occur. Although some researchers are believed that receding gum and tooth changes are associated with complications of aging, but it can be prevented easily.
Receding gum has different direct and indirect reasons. Orthodontic treatment can prevent gum recession. The type and severity of gingival tissue damage are extremely related to the periodontal approach. Although orthodontic treatment may cause some predisposing factors, there is no obvious reason that orthodontic treatment may cause receding gum alone. Because initially, your specialist orthodontist assures about your gum health, then apply for the orthodontic treatment.
How gum disease affect your smile?
When gum tissue becomes recede, the tooth’s root will become out and more sensitive. The receding gum and exposed root can significantly affect your smile.
The gingival recession not only informs you about the periodontal disease but also is a sign of other functional problems that should be considered.
Since the receding gum occurs gradually, most people don’t realize they are affected until they experience tooth sensitivity and see the exposed roots. If your teeth look longer than normal, it can be due to gum recession. You can feel a small hole around your tooth line.
Receding gum risk factors
The improper tooth brushing can cause a gum line recession. Over time it will be considered as chronical trauma. In some situations, the local gum recession can create by reducing alveolar bone thickness. Also, the sudden increase in dental plaque, poor oral hygiene or insufficient brushing is considered as gum recession risk factors. Following are some other items that can cause gum recession including:
- Periodontal disease
- Genetic
- Improper brushing
- Poor oral hygiene
- Hormone changes
- Smoking
- Tooth-chattering and putting extreme force on teeth
What is gum graft surgery?
This is a surgical procedure to reverse the gum recession. Gum graft surgery is recommended for advanced or moderate periodontal diseases. First, the non-surgery treatment is applied, if it does not work, the gum graft surgery comes as the second option.
Regeneration
As the gum volume is decreased, a regenerative material such as membrane, tissue graft or tissue-stimulating protein is used to regenerate damaged bone and tissue.
Soft tissue graft
This procedure contains using oral tissue or nearby healthy gum tissue to encourage and regenerate the gum tissue.
Preparation for gum surgery
Initially, your periodontist or dentist will remove all plaques from the surrounding teeth and make sure about your oral health. Then your periodontist will check your general health and current medications.
Do gum graft prevent receding gum?
In fact, gum grafts can’t treat gum recession alone. Initially, the receding factors should be removed then the gum graft surgery will be applied. Since the gum grafts contain thickness tissue, there is a risk to open the wound without primary treatment.
Receding gum prevention

There are some factors that help you to prevent gum recession such as proper diet and oral hygiene as well as the following items including:
- Appropriate brushing
- Align disordered and rough teeth or blocking the space between teeth by orthodontic treatment
- Regular oral health check-ups
- Stop smoking
- Use an electric or soft toothbrush
- A regular visit with your dentist or periodontist
How is gum surgery performed?
First, your periodontist checks the damaged area then uses a scalpel to separate the gum from the tooth. They will be lifted or fold back as a flap. So your periodontist is able to access the roots and bones that support teeth. Then inflamed tissue will be removed from the teeth and any holes in the bone. If you have any bone defects your periodontist may remove them and smooth the edges of the bone by using files or rotating burs. Finally, the gum will be placed against the teeth in their primary location. Some periodontists use stitches that dissolve on their own or use stitches that should be removed after 10 days.
Follow up after gum surgery
After the surgery, you may have mild or moderate pain that your surgeon will prescribe you a painkiller. It is very important to keep your mouth clean during the recovery time. It’s better to use soft toothbrushes in order to remove the plaque gently from your teeth. Using anti-microbial mouth washer containing chlorhexidine is recommended after periodontal surgery because they kill bacteria and delay the plaque growth and help your mouth to heal sooner. You may have swelling during the first days after the surgery but it will be decreased by putting the ice pack on the treated place. In some cases, the antibiotic can be prescribed to prevent infection. You should assure to use them according to the instructions because your periodontist will check that area during 7-10 days following the surgery.
Gum surgery risks
Bleeding or swelling are unavoidable risks after the surgery. There is also the risk of infection in your gums or in the area that is under the treatment, but it may decrease over time. The treated teeth may be more sensitive to the hot and cold. Feeling the pain and even minor bleeding during 48 hours after the surgery is normal conditions but these symptoms will subside after a few days. If the bleeding doesn’t stop or symptoms get worse, it may be due to infection. In this condition, you should contact your periodontist as soon as possible.